Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the most prevalent form of heart disease and one of the leading causes of death worldwide. It is a condition that develops when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the build-up of plaque. This plaque consists of cholesterol, fatty deposits, and other substances. The reduction in blood flow can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or other symptoms and, in severe cases, can lead to a heart attack or Congestive Heart Failure. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for CAD is essential for preventing and managing its impact across different age groups and genders.
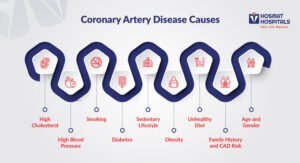
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease
The primary cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, a process characterized by the build-up of plaque within the arterial walls. Several factors that contribute to this condition include:
High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can lead to plaque formation in the arteries.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension damages the inner lining of the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque build-up.
Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that can damage the blood vessels and lead to atherosclerosis. It also lowers the level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol.
Diabetes: Elevated blood sugar levels can harm blood vessels and raise the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to several CAD risk factors, including high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes.
Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes, all of which increase the risk of CAD.
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries.
Family History and CAD Risk: Having a family history of heart disease heightens the risk of developing CAD.
Age and Gender: The risk of CAD rises with age, with men typically facing a higher risk compared to pre-menopausal women. However, the risk for women increases and may surpass that of men after menopause.
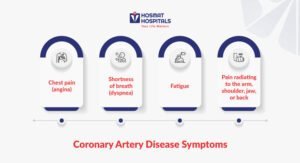
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
CAD can develop gradually, and in some cases, there might not be any noticeable symptoms in the early stages. Age and gender may influence the progression of the disease, potentially leading to the following experiences as it advances:
Chest pain (angina): This is the most common symptom, often described as a squeezing, pressure, or tightness in the chest. It can be triggered by physical activity, emotional stress, and sometimes even cold weather.
Shortness of breath (dyspnea): You may feel a lack of air, especially during exertion or even at rest in advanced CAD.
Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness can be a sign that your heart isn’t getting the oxygen it needs.
Pain radiating to the arm, shoulder, jaw, or back: Angina pain can sometimes extend beyond the chest.
Treatment Options for Coronary Artery Disease
The treatment of CAD focuses on managing symptoms, reducing risk factors, and preventing complications. Treatment options include:
Lifestyle modifications: Quitting smoking, adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and rich in fruits and vegetables, and engaging in regular physical activity are the cornerstones of managing CAD.
Medications: Cholesterol-lowering medications like statins can help control LDL levels. Other medications may be prescribed to manage blood pressure, reduce chest pain, and prevent blood clots.
Minimally invasive procedures: Techniques like angioplasty and stenting can open narrowed arteries by inserting a small balloon to widen the blockage and placing a stent to keep the artery open.
Coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG): In severe cases, CABG might be necessary to create a detour around blocked arteries using blood vessels from other parts of the body.
Conclusion
Coronary Artery Disease is a serious condition that requires attention and management to prevent severe outcomes such as heart attacks. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the various treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their heart health. Regular medical check-ups and adhering to a heart-healthy lifestyle are fundamental in the fight against CAD.
At HOSMAT Hospitals, the best Multispeciality Hospitals in Bangalore, we are dedicated to your heart health. Our Department of Cardiac Sciences, renowned for excellence and cutting-edge treatments, is here to provide comprehensive care for Coronary Artery Disease. Schedule a consultation with our expert cardiologists today and take the first step towards a healthier heart.