Atherosclerosis is a significant health concern globally, contributing to various cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Despite its prevalence, there is often confusion about what atherosclerosis entails, its symptoms, causes, and how it can be treated. This blog aims to provide a clear, detailed understanding of atherosclerosis, equipping readers with the knowledge to recognize, manage, and seek appropriate care for this condition.
What is Atherosclerosis?
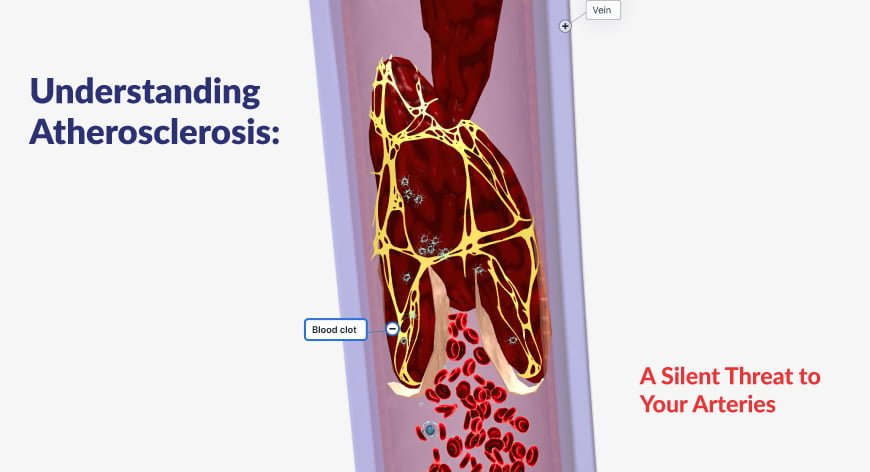
Atherosclerosis is a condition marked by the accumulation of plaque inside the walls of the arteries. Plaque consists of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and various other substances present in the bloodstream. Over time, this buildup can harden and narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs and tissues. The condition can affect any artery in the body, including those of the heart, brain, arms, legs, and kidneys, leading to severe health complications.
Symptoms
Atherosclerosis often progresses silently, without symptoms, until a significant blockage or rupture occurs. When symptoms do manifest, they vary depending on which arteries are affected:
- Coronary arteries: Chest pain or angina, shortness of breath, heart attack.
- Carotid arteries: Sudden numbness or weakness in arms or legs, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, temporary loss of vision in one eye, drooping muscles in your face (signs of a stroke).
- Peripheral arteries: Leg pain when walking (claudication), decreased blood pressure in affected limbs, numbness.
- Renal arteries: High blood pressure, kidney failure.
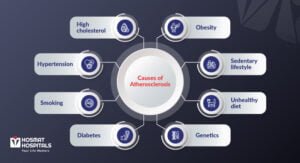
Causes
Several factors contribute to atherosclerosis, including:
- High cholesterol: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can lead to plaque formation.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage the inner lining of arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
- Smoking: Chemicals in tobacco smoke damage blood vessels and increase plaque formation.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels and promote atherosclerosis.
- Obesity: Excess weight contributes to other risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise contributes to the development of many risk factors for atherosclerosis.
- Unhealthy diet: Consuming a diet rich in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol leads to the accumulation of plaque.
- Genetics: Family history of heart disease or stroke can increase the risk.
Treatments
Treatment for atherosclerosis aims to reduce plaque buildup, prevent blood clots, and improve symptoms. It includes lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical procedures:
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: Consuming a diet that is low in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium supports heart health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps improve cardiovascular health and manage weight.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can halt the progression of atherosclerosis and reduce risk.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight helps control blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
Medications
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels and stabilize plaques.
- Antihypertensives: Control high blood pressure to prevent further arterial damage.
- Antiplatelet agents: Reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Diabetes medications: Manage blood sugar levels.
Surgical Procedures
- Angioplasty and stent placement: A catheter is used to open blocked arteries and insert a stent to keep them open.
- Bypass surgery: Redirects blood flow around a blocked artery using a vessel graft from another part of the body.
- Endarterectomy: The process of removing plaque from an artery’s inner lining.
Conclusion
Atherosclerosis is a silent yet potentially deadly condition that necessitates awareness and proactive management. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can empower individuals to take control of their cardiovascular health. Early detection and intervention by the Department of Cardiac Sciences are crucial in preventing severe complications such as congestive heart failure, heart attacks and strokes.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of atherosclerosis or are at risk, don’t wait. Schedule a consultation with our experienced cardiologists at HOSMAT Hospitals, the best Multispeciality Hospitals in Bangalore, today. Together, we can take the necessary steps to protect your heart and overall health.
Disclaimer: This blog is intended for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. When in doubt about a medical condition, consult your physician or other qualified healthcare providers.