Gastroesophageal reflux disease, often shortened to GERD, is a common digestive complaint that can significantly impact your quality of life. The condition occurs when stomach acid backs up into the oesophagus, which connects your mouth to your stomach. This backwash of acid irritates the lining of the oesophagus, leading to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms.
Understanding GERD: A Breakdown
The lower oesophagal sphincter (LES) is a muscular valve located at the end of the oesophagus. Ideally, the LES remains closed, except when food and liquids pass through to the stomach. In GERD, the LES weakens or relaxes inappropriately, allowing stomach contents, including acid, to flow back into the oesophagus. This recurrent reflux is the hallmark of GERD.
Causes of GERD
The following factors can lead to GERD development:
- Hiatal hernia: This occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm, the muscle separating the chest from the abdomen, weakening the LES.
- Diet: Certain foods, such as spicy or fatty meals, chocolate, peppermint, and acidic beverages like coffee and citrus juices, can relax the LES and worsen symptoms.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on the abdomen, pushing stomach contents upwards.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can weaken the LES.
- Scleroderma: This autoimmune disease can affect the connective tissue in the esophagus, impacting its function.
- Medications: Certain medications, like some blood pressure medications and muscle relaxants, can contribute to GERD.
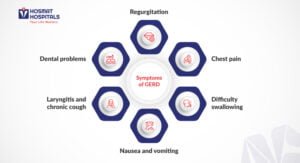
Symptoms of GERD
The classic symptom of GERD is heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest that often worsens after eating or lying down. However, GERD can manifest in various ways, including:
- Regurgitation: A sour or bitter taste in the mouth caused by stomach contents flowing back into the esophagus.
- Chest pain: GERD can sometimes mimic chest pain associated with angina (heart-related pain).
- Difficulty swallowing: Chronic irritation from acid reflux can cause the esophagus to narrow, making swallowing difficult.
- Nausea and vomiting: In severe cases, GERD can lead to nausea and vomiting.
- Laryngitis and chronic cough: Refluxed acid can irritate the voice box (larynx), causing hoarseness and a chronic cough.
- Dental problems: Acid reflux can erode tooth enamel, leading to dental issues.
If you experience any of these symptoms frequently, particularly heartburn that occurs more than twice a week, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and proper treatment.
Treatment Options for GERD
The treatment of GERD aims to reduce symptoms, heal esophagal damage, and prevent complications. The approach may include lifestyle modifications, medications, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary changes: Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding trigger foods.
- Weight loss: Reducing abdominal pressure by losing excess weight.
- Elevating the head of the bed: Sleeping with the head elevated can prevent nighttime reflux.
- Avoid lying down after meals: Waiting at least three hours after eating before lying down or going to bed.
- Quitting smoking: Reducing nicotine intake to strengthen the LES.
Medications
- Antacids: Over-the-counter medicines that neutralize stomach acid and provide quick relief.
- H2 receptor blockers: Medications that reduce acid production, available over-the-counter or by prescription.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): Stronger acid blockers that promote healing of the esophagus, available by prescription.
- Prokinetics: Medications that help strengthen the LES and speed up stomach emptying.
Surgical Treatments
- Fundoplication: The surgical procedure of wrapping the stomach’s top around the LES to prevent reflux.
- LINX device: A ring of magnetic beads placed around the LES to reinforce the sphincter and prevent acid reflux.
Conclusion
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease is a manageable condition with a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and potentially Gastrointestinal surgery. Understanding the causes and symptoms of GERD is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. If you experience frequent acid reflux or other symptoms of GERD, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
If you or a loved one is struggling with GERD, don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Contact our team of gastroenterology specialists at HOSMAT Hospitals, the best multi-speciality hospital in Bangalore, today to schedule a comprehensive evaluation and begin your journey toward relief and improved digestive health.